What is Centralized Finance (CeFi)?


Centralized Finance (CeFi) refers to financial services operated by centralized entities, where a third‑party intermediary manages the custody, transactions, and processes of users’ assets. This model contrasts with decentralized finance (DeFi), where intermediaries are replaced by code and blockchain protocols. While CeFi offers familiarity and stability, it comes with unique risks, especially relating to security, governance, and operational failures. Understanding how CeFi protocols and platforms operate is essential for crypto users, investors, and anyone involved in digital finance. In this article, we will examine CeFi’s architecture, its market structure, advantages, disadvantages, and risks, as well as a comparison to DeFi.
What is CeFi?
At its core, CeFi is a model where a centralized entity, such as a crypto exchange (e.g., Binance, Kraken), lending platform, or payment processor, acts as an intermediary between the end user and the financial system. These entities provide various services such as:
A CeFi platform typically provides an API layer, user interfaces, and liquidity pools. It also ensures that all financial activity complies with regulatory standards, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML).
Why Do We Need CeFi?
Centralized Finance (CeFi) is often considered a bridge between traditional financial systems and the emerging blockchain ecosystem. While DeFi provides a decentralized and permissionless environment, it has barriers related to liquidity, technical barriers, and regulatory constraints. In contrast, CeFi platforms play a critical role by offering:
CeFi vs DeFi: Key Differences and Similarities
Understanding CeFi vs DeFi highlights the tradeoffs between centralized platforms and decentralized alternatives.
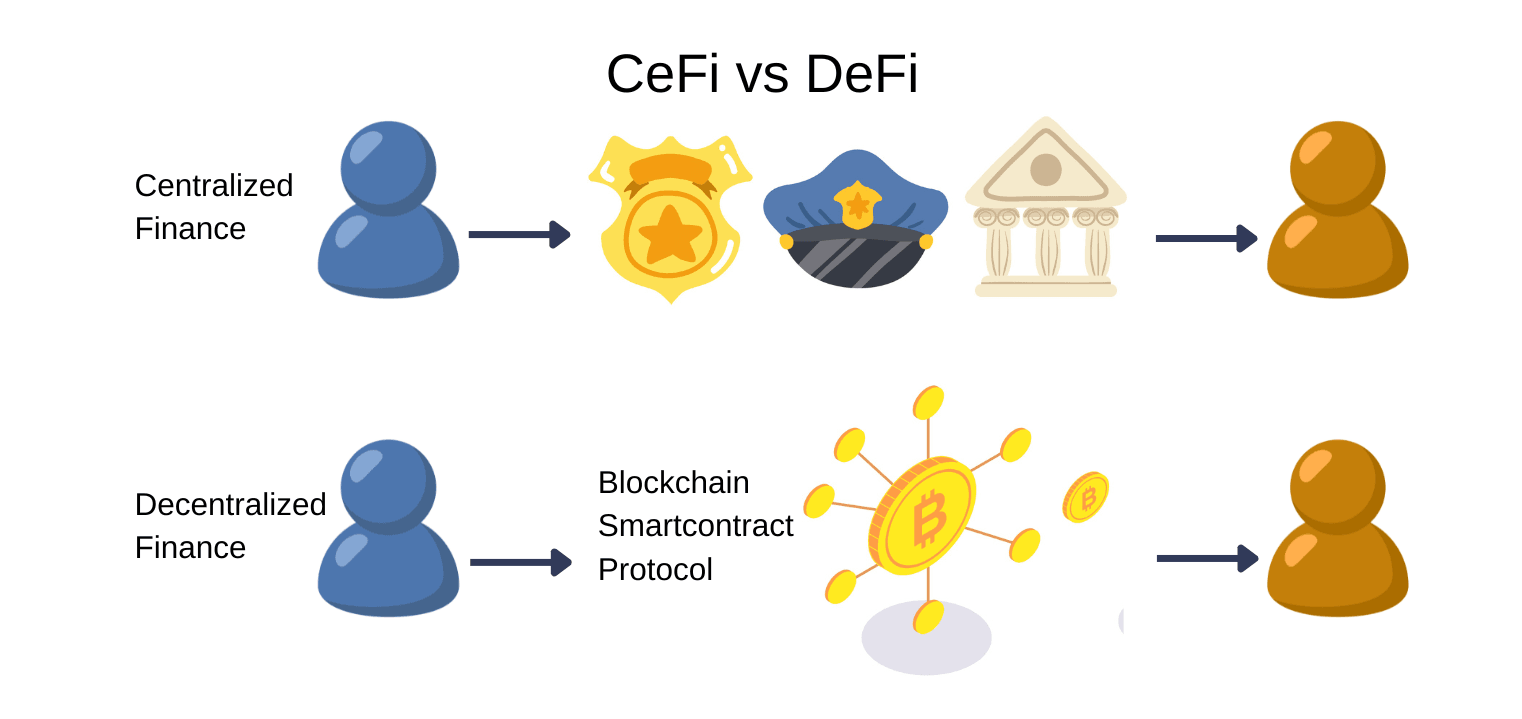
Key Differences
DeFi vs CeFi:
| Title | DeFi | CeFi |
|---|---|---|
| Cryptocurrency trading | ✓ | ✓ |
| Derivatives trading | ✓ | ✓ |
| Instant Settlement | ✓ | ✓ |
| Fiat-to-crypto | ✓ | ✓ |
| Non-custodial | ✓ | ✗ |
| Cross-chain solutions | ✓ | ✓ |
| Transparency of transactions | ✓ | ✗ |
| Mandatory know-your-customer requirements | ✗ | ✓ |
| Blockchain Switching Headache | ✓ | ✗ |
| Payments | ✓ | ✓ |
Key Similarities
How does CeFi work?
CeFi operates via a centralized intermediary that manages all aspects of financial transactions and assets. Here’s an overview of how a typical CeFi platform works:
Advantages and Disadvantages of CeFi
Advantages
Disadvantages
What are the risks in CeFi?
Centralized finance (CeFi) platforms offer convenience and liquidity but expose users to unique vulnerabilities. These risks stem from trusting a single entity rather than decentralized code.
Platform-Specific Risks
Regulatory and Legal Risks
Security Threats in Centralized Systems
Future of CeFi in 2025 and Beyond
The next phase of centralized finance (CeFi) will not be about replacing DeFi, but about adapting, integrating, and coexisting with it. CeFi players are increasingly pressured to innovate while navigating security, regulation, and liquidity challenges.
-Institutional DeFi Gateways: CeFi exchanges are embedding DeFi services (staking, yield products, lending pools) while offering user-friendly custodial access.
-Tokenized Assets: Expect broader adoption of real-world assets (RWAs) like tokenized bonds, equities, and stablecoins as CeFi bridges traditional finance with on-chain markets.
-Custodial Smart Contracts: Funds held in semi-transparent, auditable contracts reduce trust assumptions.
-Multi-Party Computation (MPC): Spreads key management across multiple parties, minimizing single points of compromise.
-Proof of Reserves (PoR): Transparent, cryptographic attestations of exchange holdings are becoming industry standards to rebuild trust post-FTX.
-Global Coordination: With MiCA in the EU and FSMA updates in the UK, CeFi must comply with converging but fragmented regulations.
-Compliance-as-a-Service: Exchanges may adopt on-chain KYC/AML modules, balancing compliance with privacy preservation.
-CeFi–DeFi Liquidity Hubs: Centralized platforms will act as liquidity routing engines, tapping both order books and AMM pools.
-Cross-Chain Settlement: CeFi will rely on bridges and interoperability protocols (e.g., LayerZero, Axelar) to offer seamless multi-chain access.
By 2025 and beyond, CeFi’s success will depend on whether it can regain user trust through transparency and adopt the best of DeFi’s innovations without sacrificing security or compliance. Rather than a rivalry, CeFi and DeFi are on track to co-evolve into a blended financial ecosystem.
Is CeFi Safe for Beginners?
For newcomers, CeFi platforms are often the entry point into crypto because they provide familiar user experiences: simple interfaces, customer support, fiat on-ramps, and regulatory oversight. Compared to DeFi’s steep learning curve, CeFi feels safer.
However, safety in CeFi is not guaranteed. Users must understand the custodial trade-off: the platform controls their funds, not them. This creates both convenience and risk.
Understanding Security Protocols
When choosing a CeFi exchange or broker, beginners should verify that the platform employs industry-standard protections:
Steps Beginners Can Take to Protect Their Investments
Even the most secure platforms can fail. Beginners can minimize risks with a few proactive steps:
Summary
Centralized Finance (CeFi) serves as the traditional model for crypto‑based financial services, offering users accessibility, regulatory clarity, and liquidity. However, the tradeoffs, centralized control, security risks, and high fees make it essential for users to understand both the advantages and risks associated with these platforms. CeFi platforms are crucial in driving mainstream adoption of crypto by providing familiar, trusted environments while integrating decentralized technologies.
Resources
Frequently asked questions
Check out most commonly asked questions, addressed based on community needs. Can't find what you are looking for?
Contact us, our friendly support helps!
How secure is CeFi for beginners?
CeFi offers simplicity and user‑friendly security features like customer support, regulatory compliance, and built‑in fraud prevention. However, users must understand the risks associated with custodial services.
What is the biggest risk in using CeFi?
The biggest risk in CeFi is custodial risk, meaning the platform controls the assets. If the platform fails, is hacked, or is shut down, users may lose their funds.
How do I choose a CeFi platform?
Evaluate platforms based on their regulatory compliance, security protocols, insurance policies, and reputation within the industry.