Top 10 Blockchain Innovations Driving Market Growth in 2025


Blockchain is shifting from novelty to infrastructure where auditability, programmable settlement, and interoperability matter. Adoption tracks real constraints, latency, compliance, and recoverability, rather than speculation. Gains come from rollups + data-availability cutting costs, smart contracts automating routine tasks, and identity/provenance checks without excess disclosure. Tokenized real-world assets move ahead under clearer rules, while supply-chain and healthcare rely on verifiable records, the sections below unpack trends, trade-offs, and safeguards.
Emerging Blockchain Trends Shaping the Future
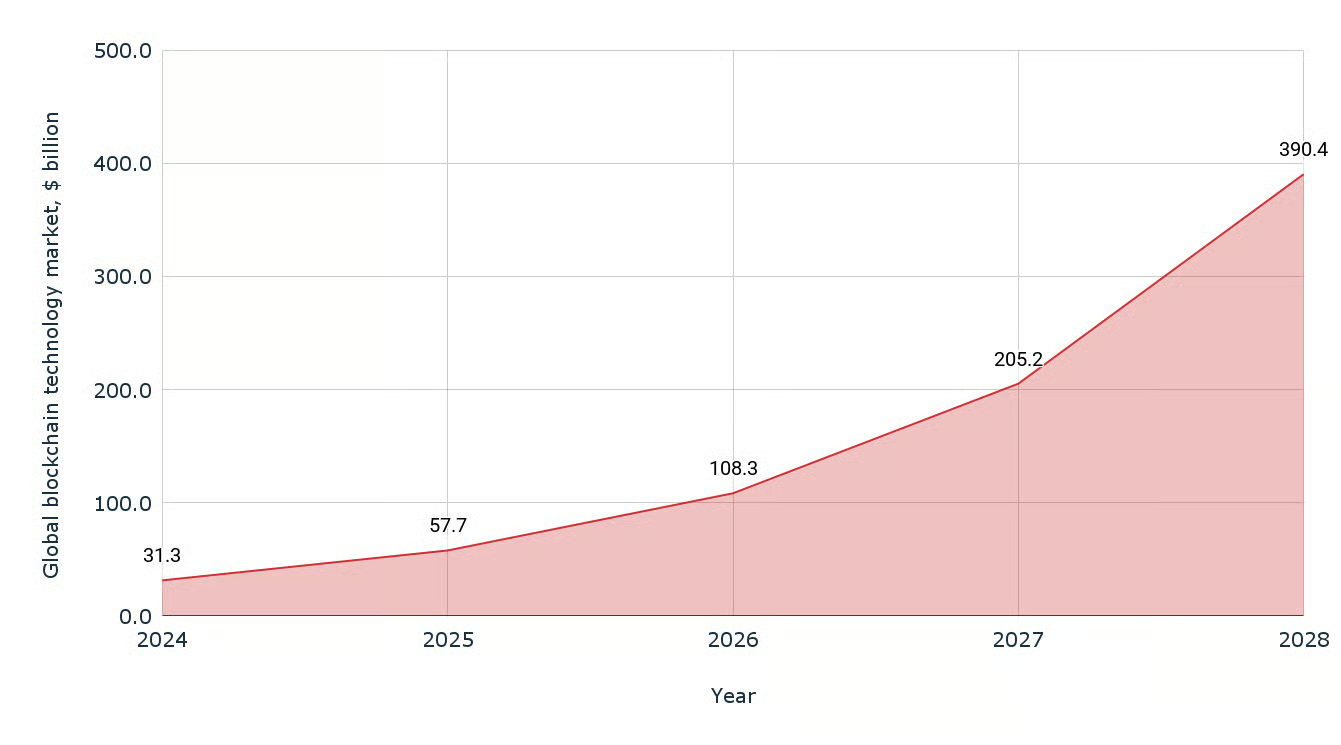
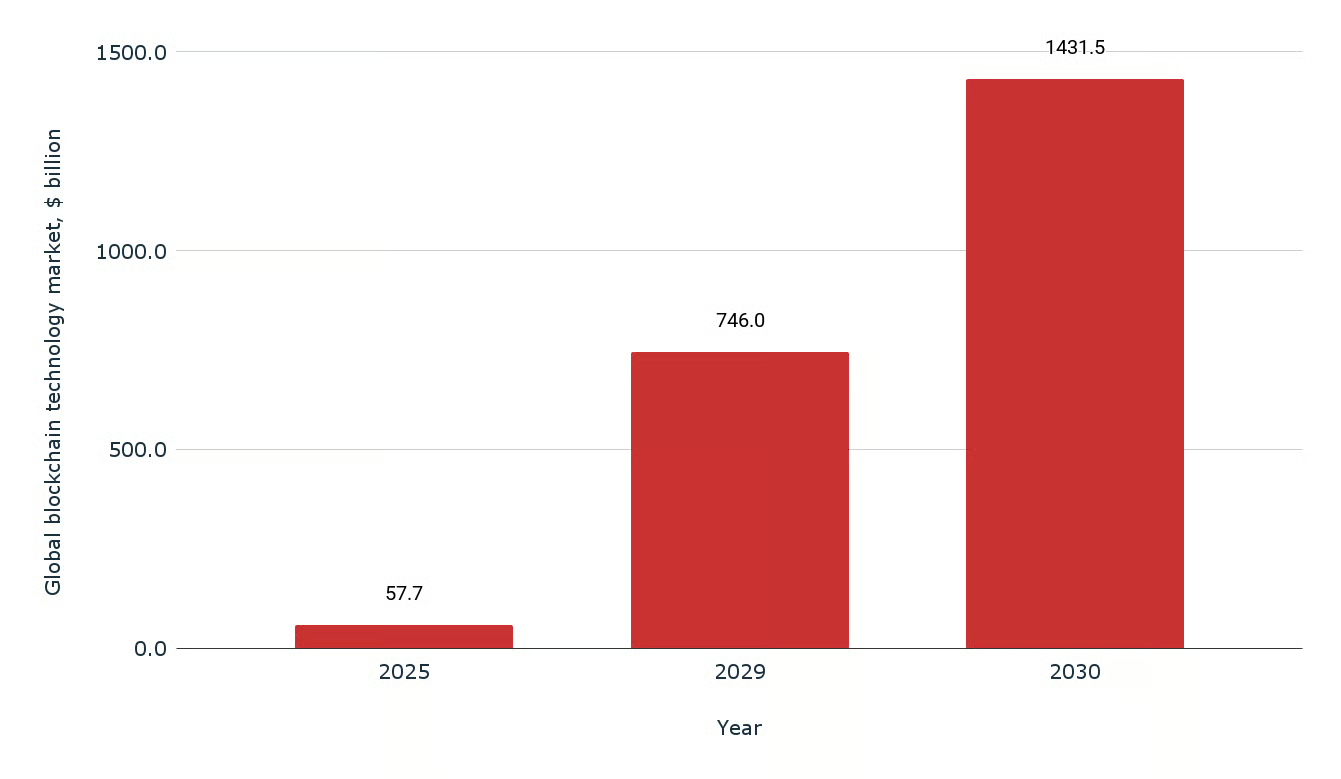
A pivot from speculative cycles to operational deployment has been observed throughout 2025, as blockchain innovations are being integrated where verifiable records and programmable settlement increase reliability. It may be tempting to assume that market growth is driven solely by token prices; yet, in practice, throughput, auditability, and integration cost have governed adoption. Rollups (batched off-chain execution with on-chain proofs) and data-availability layers are being paired to reduce fees by an order of magnitude while retaining finality measured in seconds rather than milliseconds. Interoperability frameworks are enabling assets and messages to move across chains, and rate limiting (a cap on requests per time window) is being applied to avoid congestion during traffic spikes. The effect is a gradual normalization: blockchain is being treated as an infrastructure layer, not a spectacle.
Enterprise Adoption of Blockchain Technology
Enterprise adoption has accelerated where blockchain is embedded behind familiar controls. Document registries are being anchored with on-chain hashes (fixed-length fingerprints) while original files remain in governed storage, which improves audit trails without altering user workflows. In finance and trade operations, programmable escrow via smart contracts (self-executing code bound to conditions) is replacing email-based approvals, reducing settlement windows from days to minutes under typical loads. Private and consortium chains are being favored when data residency and access control are paramount, while public chains are being tapped for settlement assurances and ecosystem reach. The trade-off is clear: greater control and compliance alignment are achieved on restricted networks, while broader composability and liquidity are obtained on open ones.
How Supply Chain Management Benefits from Blockchain Integration
In supply chains, end-to-end traceability is being strengthened by immutable event logs that follow a unit from production to receipt. Under constrained bandwidth, light-client modes are being used to submit minimal proofs while full data is synchronized later. Temperature excursions recorded by IoT sensors (networked devices capturing environment data) are being correlated with custody handoffs, narrowing recalls to affected lots rather than entire shipments. The comparison dimension that matters most has been provenance auditability, not raw transaction volume. A micro-scenario illustrates the pattern: a small test shipment was registered before a nationwide rollout; variance between expected and scanned checkpoints was measured, thresholds were tuned, and only then was mainline traffic cut over, an approach that reduced exception handling by a measurable margin.
Smart Contracts Transforming Business Operations
The most practical impact of smart contracts has been the reliable execution of routine obligations. Volume-based rebates are being released automatically once usage thresholds are crossed, and supplier payments are being gated on digitally signed delivery proofs. Unexpected behavior has been encountered when cross-chain timeouts differ; therefore, canary deployments were promoted first, and on-chain feature flags (runtime toggles in contract storage) were used to stage activations. Where upgradeability is required, proxy patterns are being employed to preserve addresses while allowing logic revisions; the additional key-management burden has been acknowledged and mitigated through multi-signature policies (N-of-M approvals). A brief payment flow is typical: a nominal “penny test” was sent, the contract state was simulated (a dry-run preview) to validate fees, a transient gas spike was detected, and the primary transfer was deferred until conditions stabilized.
Blockchain's Role in Enhancing Cybersecurity
A reduction in centralized attack surfaces has been recorded where verification is pushed to the edges of the network. Decentralized identifiers, or DIDs (user-controlled identity anchors), and verifiable credentials (digitally signed attestations) are being used so that fewer systems need to store raw personal data. A correlation has been observed between data minimization and lower breach exposure. However, phishing pressure has shifted toward signing prompts, which has required clearer transaction previews, spend limits, and anomaly detection to be presented before confirmation.
Leveraging blockchain for secure identity management
With DIDs, identity proofs are being bound to cryptographic keys controlled by users, and selective disclosure (revealing only the required attribute) is being practiced. For example, age-over-18 status can be proved without exposing birthdates. Revocation lists are being published on-chain so compromised credentials can be invalidated globally within minutes. The practical trade-off appears between privacy and recoverability: strong non-custodial control improves privacy, while social or institutional recovery is needed to reduce lockout risk; hybrid approaches are therefore being adopted.
Preventing fraud and data breaches with blockchain
Tamper-evident ledgers are being used to detect record manipulation attempts, and transaction simulation is being shown to users to expose approval side effects in advance. Protected mempools (routing that limits miner-extractable value, or MEV, profit from reordering transactions) are being used for sensitive trades. Threshold alerts, such as gas-price ceilings, maximum transfer sizes, or velocity limits, are being enforced at the wallet and policy layers. These safeguards do not eliminate fraud but reduce its viable surface.
Tokenization and Digital Assets in the Evolving Economy
Tokenization is converting claims on cash flows and assets into transferable digital units, increasing liquidity and enabling fractional participation. Transfer restrictions and disclosure rules are being encoded to reflect legal constraints, and off-chain registrars are being reconciled with on-chain states to preserve finality.
The principal benefit is access: smaller positions can be entered or exited without full-asset sales, while the main cost lies in governance, where compliance artifacts must be synchronized and auditable with low error rates.
Rise of real-world asset tokenization
Receivables, inventory, and property interests are being tokenized so that partial ownership can be traded in lots as small as sub-1% units. Settlement times have been shortened to minutes, subject to chain finality settings, and coupon or dividend distributions are being automated by contract schedules. Pricing transparency improves when secondary markets display order books, though liquidity remains path-dependent; market depth is being observed to correlate with standardized disclosures and consistent reporting cadences.
How non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are reshaping industries?
NFTs are shifting from collectibles toward utility entitlements. Access to datasets, software licenses, and event capacity is being granted via token checks at the application layer. Royalties encoded on-chain are being honored where marketplaces implement the logic; otherwise, off-chain enforcement has been required. The comparison dimension has moved from aesthetic scarcity to cross-platform enforceability and revocation control.
Government Regulations and Their Influence on Blockchain Growth
Policy clarity has been expanding, and with it, enterprise comfort. Travel-rule compliance (identity data accompanying transfers above stated thresholds) is being integrated at wallet and gateway layers. Tax-lot calculation rules are being standardized, which reduces reconciliation friction. Fragmentation persists across jurisdictions, so geofencing and region-specific policy bundles are being embedded into access controls. As guidance stabilizes, implementation cycles shorten because audit scope becomes predictable.
Impact of global regulatory frameworks on blockchain adoption
Where licensing regimes and reporting templates are defined, onboarding timelines are being reduced from quarters to weeks. Conversely, uncertainty has been shown to delay deployments, as legal review cycles extend and contingency architectures multiply. The implication is straightforward: adoption rises where controls are prescriptive, testing sandboxes are available, and supervisory expectations are published with examples.
To Sum Up
Across 2025, growth in the blockchain market has been propelled less by spectacle and more by steady replacement of brittle, email-driven processes with verifiable, programmable rails. The most dependable gains have appeared where small, reversible tests were favored before large, irreversible actions; where previews were read when exposure was nontrivial; and where identifiers were confirmed prior to transfer. No universal “best chain” can be asserted; selection should be guided by named criteria, latency tolerance, auditability requirements, integration complexity, and regulatory fit. Two compact heuristics have been validated in practice: simulate before signing, and defer when signals deviate from normal ranges. Under these habits, innovations in scalability, identity, tokenization, and policy alignment can be implemented with higher confidence and lower operational risk.
Resources
Frequently asked questions
Check out most commonly asked questions, addressed based on community needs. Can't find what you are looking for?
Contact us, our friendly support helps!
What are the main benefits of decentralized finance (DeFi)?
DeFi lets anyone with a wallet access financial services without intermediaries, offering:
How does blockchain improve supply chain management?
It creates a shared, tamper-evident ledger across suppliers, shippers, and retailers, enabling end-to-end traceability of goods, auditable data integrity, automated workflows via smart contracts (like releasing payment on verified delivery), quicker and more targeted recalls, reduced fraud and errors through a single source of truth, and better access to financing with real-time, trusted status updates.
What is the role of smart contracts in business operations?
Smart contracts help businesses operate with more speed, efficiency, and reliability, while cutting out a lot of the friction and trust issues that normally slow operations down. They’re like giving your business processes a robotic exoskeleton, stronger, faster, and way less messy.
Smart contracts are like “set-it-and-forget-it” business rules that execute automatically. They remove manual steps, speed up transactions, cut intermediaries and fees, and boost trust through built-in transparency and security. The result: faster, cleaner, and more reliable business operations with far less friction.




